Draw Call 问题:每个独立网格对象都会产生一次渲染调用
内存占用:大量独立对象占用更多内存
GPU 负载:频繁的状态切换降低渲染效率
大幅减少 Draw Call 数量
提升渲染性能,特别是大量相似对象
减少内存占用
javascript
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { BufferGeometryUtils } from 'three/examples/jsm/utils/BufferGeometryUtils.js';
// 创建多个几何体
const geometries = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1);
geometry.translate(
Math.random() * 50 - 25,
Math.random() * 50 - 25,
Math.random() * 50 - 25
);
geometries.push(geometry);
}
// 合并几何体
const mergedGeometry = BufferGeometryUtils.mergeBufferGeometries(geometries);
// 创建材质
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 });
// 创建网格
const mergedMesh = new THREE.Mesh(mergedGeometry, material);
scene.add(mergedMesh);javascript
// 注意:THREE.Geometry 在 r125+ 已废弃
const mergedGeometry = new THREE.Geometry();
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
const box = new THREE.Mesh(
new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial()
);
box.position.set(
Math.random() * 50 - 25,
Math.random() * 50 - 25,
Math.random() * 50 - 25
);
box.updateMatrix();
mergedGeometry.merge(box.geometry, box.matrix);
}javascript
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1);
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 });
const count = 1000;
// 创建实例化网格
const instancedMesh = new THREE.InstancedMesh(geometry, material, count);
// 为每个实例设置变换矩阵
const matrix = new THREE.Matrix4();
const position = new THREE.Vector3();
const quaternion = new THREE.Quaternion();
const scale = new THREE.Vector3(1, 1, 1);
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
position.set(
Math.random() * 100 - 50,
Math.random() * 100 - 50,
Math.random() * 100 - 50
);
quaternion.setFromEuler(
new THREE.Euler(
Math.random() * Math.PI,
Math.random() * Math.PI,
Math.random() * Math.PI
)
);
matrix.compose(position, quaternion, scale);
instancedMesh.setMatrixAt(i, matrix);
}
// 重要:设置 instanceMatrix 需要更新
instancedMesh.instanceMatrix.needsUpdate = true;
scene.add(instancedMesh);javascript
const instancedMesh = new THREE.InstancedMesh(geometry, material, count);
const color = new THREE.Color();
// 设置每个实例的颜色
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
color.setHSL(Math.random(), 0.8, 0.6);
instancedMesh.setColorAt(i, color);
}
if (instancedMesh.instanceColor) {
instancedMesh.instanceColor.needsUpdate = true;
}javascript
class OptimizedSceneManager {
constructor() {
this.nearObjects = new THREE.Group();
this.farObjects = new THREE.Group();
this.lodLevels = [];
this.initLODSystem();
}
initLODSystem() {
// 近处:高细节几何体
const highDetailGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1, 10, 10, 10);
const highDetailMaterial = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: 0xff0000,
roughness: 0.1,
metalness: 0.8
});
// 远处:低细节几何体(合并)
const lowDetailGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2);
const lowDetailGeometries = this.createInstances(lowDetailGeometry, 500);
const mergedLowDetailGeometry = BufferGeometryUtils.mergeBufferGeometries(lowDetailGeometries);
const lowDetailMaterial = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: 0x00ff00,
flatShading: true
});
// 创建LOD对象
const lod = new THREE.LOD();
const highDetailMesh = new THREE.Mesh(highDetailGeometry, highDetailMaterial);
const lowDetailMesh = new THREE.Mesh(mergedLowDetailGeometry, lowDetailMaterial);
lod.addLevel(highDetailMesh, 0);
lod.addLevel(lowDetailMesh, 50);
scene.add(lod);
}
}javascript
class GeometryBatchManager {
constructor(maxVertices = 65535) {
this.maxVertices = maxVertices; // WebGL限制
this.batches = new Map(); // material -> geometries
}
addObject(mesh) {
const materialKey = this.getMaterialKey(mesh.material);
if (!this.batches.has(materialKey)) {
this.batches.set(materialKey, []);
}
const batch = this.batches.get(materialKey);
batch.push(mesh);
// 检查是否需要分批
if (this.shouldCreateNewBatch(batch, mesh.geometry)) {
this.createNewBatch(materialKey);
}
}
getMaterialKey(material) {
// 根据材质属性生成唯一键
return JSON.stringify({
type: material.type,
color: material.color?.getHex(),
map: material.map?.uuid
});
}
shouldCreateNewBatch(batch, geometry) {
let totalVertices = 0;
for (const mesh of batch) {
totalVertices += mesh.geometry.attributes.position.count;
}
return totalVertices + geometry.attributes.position.count > this.maxVertices;
}
finalize() {
const mergedMeshes = [];
for (const [materialKey, meshes] of this.batches) {
const geometries = meshes.map(mesh => {
const geometry = mesh.geometry.clone();
geometry.applyMatrix4(mesh.matrixWorld);
return geometry;
});
const mergedGeometry = BufferGeometryUtils.mergeBufferGeometries(geometries);
const material = meshes[0].material;
mergedMeshes.push(new THREE.Mesh(mergedGeometry, material));
}
return mergedMeshes;
}
}javascript
class FrustumCulledInstancedMesh extends THREE.InstancedMesh {
constructor(geometry, material, count) {
super(geometry, material, count);
this.visibleInstances = new Array(count).fill(true);
this.frustumCulled = true;
}
updateInstanceVisibility(camera) {
const frustum = new THREE.Frustum();
frustum.setFromProjectionMatrix(
new THREE.Matrix4().multiplyMatrices(
camera.projectionMatrix,
camera.matrixWorldInverse
)
);
const sphere = new THREE.Sphere();
const matrix = new THREE.Matrix4();
for (let i = 0; i < this.count; i++) {
this.getMatrixAt(i, matrix);
sphere.center.setFromMatrixPosition(matrix);
sphere.radius = 1; // 根据实际几何体大小调整
this.visibleInstances[i] = frustum.intersectsSphere(sphere);
}
this.updateVisibilityAttributes();
}
updateVisibilityAttributes() {
// 可以通过自定义属性或修改颜色实现可见性控制
// 这里简化处理,实际使用时需要更复杂的实现
}
}** 大规模场景优化**
javascript
class OptimizedCityScene {
constructor() {
this.buildingGeometries = this.createBuildingGeometries();
this.treeGeometries = this.createTreeGeometries();
this.roadGeometries = this.createRoadGeometries();
this.initialize();
}
initialize() {
// 建筑物:使用 InstancedMesh
const buildingMaterial = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: 0xcccccc,
roughness: 0.7
});
this.buildingMesh = new THREE.InstancedMesh(
this.buildingGeometries.base,
buildingMaterial,
1000
);
// 树木:按类型分组合并
this.treeGroups = this.createTreeGroups();
// 道路:使用合并几何体
this.roadMesh = this.createRoadMesh();
}
createTreeGroups() {
const treeTypes = ['pine', 'oak', 'maple'];
const groups = {};
treeTypes.forEach(type => {
const geometries = this.treeGeometries[type];
const mergedGeometry = BufferGeometryUtils.mergeBufferGeometries(geometries);
const material = this.createTreeMaterial(type);
groups[type] = new THREE.Mesh(mergedGeometry, material);
});
return groups;
}
update(camera) {
// 动态LOD更新
this.updateLOD(camera);
// 视锥体剔除
if (this.buildingMesh instanceof FrustumCulledInstancedMesh) {
this.buildingMesh.updateInstanceVisibility(camera);
}
}
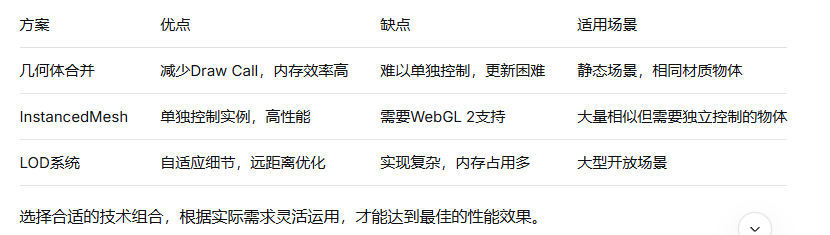
}何时使用几何体合并
✅ 大量静态、相同材质的物体
✅ 不需要单独控制的物体
✅ 性能是关键因素的场景
何时使用 InstancedMesh
✅ 需要单独控制位置/旋转/缩放
✅ 需要单独控制颜色
✅ 物体数量非常多(数千+)
✅ 需要动态更新实例属性
javascript
function monitorPerformance(renderer) {
const info = renderer.info;
console.log({
memory: info.memory,
render: {
calls: info.render.calls,
triangles: info.render.triangles,
points: info.render.points,
lines: info.render.lines
}
});
// 监控帧率
stats = new Stats();
document.body.appendChild(stats.dom);
}顶点数限制:单次Draw Call最多65535个顶点(使用Uint16)
材质限制:合并的几何体必须使用相同材质
内存管理:及时dispose不需要的几何体
更新频率:合并后的几何体难以动态更新
纹理坐标:确保合并后的UV坐标正确

BatchedMesh 是 Three.js 提供的一个高级网格类,专门用于优化大量相似对象的渲染。它基于 多绘制(Multi-Draw) 技术,将多个几何体打包到单个网格中,同时保持材质的多样性。
javascript
import { BatchedMesh } from 'three/addons/objects/BatchedMesh.js';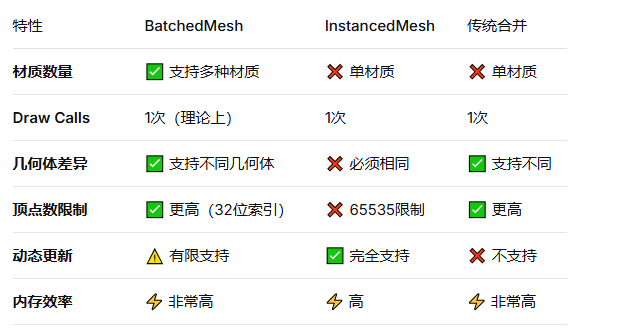
多材质支持(关键优势)
javascript
// 创建 BatchedMesh
const maxGeometryCount = 100;
const maxVertexCount = 100000;
const maxIndexCount = maxVertexCount * 1.5;
const batchedMesh = new BatchedMesh(
maxGeometryCount,
maxVertexCount,
maxIndexCount,
scene // 可选,用于材质引用
);
// 添加不同材质的几何体
const materials = [
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xff0000 }),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 }),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x0000ff })
];
// 为每个子几何体分配材质
for (let i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1);
const materialIndex = i % materials.length; // 循环使用不同材质
const batchId = batchedMesh.addGeometry(geometry, materials[materialIndex]);
// 设置变换
const matrix = new THREE.Matrix4().makeTranslation(
Math.random() * 100 - 50,
Math.random() * 100 - 50,
Math.random() * 100 - 50
);
batchedMesh.setMatrixAt(batchId, matrix);
}javascript
// 突破65535顶点限制
const batchedMesh = new BatchedMesh(
1000, // 最大几何体数量
500000, // 最大顶点数(远超65535)
1000000, // 最大索引数
scene
);
// 可以添加非常复杂的几何体
const complexGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(1, 64, 64); // 约8000个顶点javascript
// BatchedMesh 使用紧凑的存储格式
class MemoryOptimizedBatchedMesh extends BatchedMesh {
constructor() {
super(1000, 100000, 150000);
// 内部存储结构:
// - 单一顶点缓冲区
// - 单一索引缓冲区
// - 材质引用数组
// - 变换矩阵数组
}
}场景一:游戏中的建筑群
javascript
class GameCity {
constructor() {
this.batchedMesh = new BatchedMesh(500, 200000, 300000);
this.buildingTypes = this.createBuildingTypes();
this.initCity();
}
createBuildingTypes() {
// 不同类型的建筑使用不同材质
return {
residential: {
geometry: this.createResidentialGeometry(),
materials: [
new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0xf0e68c }), // 米色
new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0xd3d3d3 }), // 灰色
]
},
commercial: {
geometry: this.createCommercialGeometry(),
materials: [
new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0x87ceeb }), // 天蓝
new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0xffd700 }), // 金色
]
}
};
}
initCity() {
// 生成1000个建筑,使用不同材质
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
const type = Math.random() > 0.5 ? 'residential' : 'commercial';
const building = this.buildingTypes[type];
const materialIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * building.materials.length);
const batchId = this.batchedMesh.addGeometry(
building.geometry,
building.materials[materialIndex]
);
// 随机位置和大小
const matrix = new THREE.Matrix4()
.makeScale(
0.5 + Math.random() * 2,
1 + Math.random() * 10,
0.5 + Math.random() * 2
)
.setPosition(
Math.random() * 200 - 100,
0,
Math.random() * 200 - 100
);
this.batchedMesh.setMatrixAt(batchId, matrix);
}
scene.add(this.batchedMesh);
}
}场景二:植被系统
javascript
class VegetationSystem {
constructor() {
this.batchedMesh = new BatchedMesh(2000, 300000, 450000);
this.plantTypes = this.createPlantTypes();
this.populateTerrain();
}
createPlantTypes() {
return {
tree: {
geometries: this.createTreeGeometries(), // LOD几何体数组
materials: [
this.createLeafMaterial(),
this.createBarkMaterial()
]
},
bush: {
geometries: this.createBushGeometry(),
materials: [this.createBushMaterial()]
},
grass: {
geometries: this.createGrassGeometry(),
materials: [this.createGrassMaterial()]
}
};
}
populateTerrain() {
const terrainSize = 1000;
const density = 0.01; // 植物密度
for (let x = -terrainSize/2; x < terrainSize/2; x += 10) {
for (let z = -terrainSize/2; z < terrainSize/2; z += 10) {
if (Math.random() < density) {
this.addPlant(x, z);
}
}
}
}
addPlant(x, z) {
const plantType = this.getPlantTypeForLocation(x, z);
const plant = this.plantTypes[plantType];
// 选择LOD级别
const lodLevel = this.calculateLODLevel(x, z);
const geometry = plant.geometries[lodLevel];
const batchId = this.batchedMesh.addGeometry(
geometry,
plant.materials[Math.floor(Math.random() * plant.materials.length)]
);
// 随机变换
const scale = 0.8 + Math.random() * 0.4;
const rotationY = Math.random() * Math.PI * 2;
const matrix = new THREE.Matrix4()
.makeRotationY(rotationY)
.scale(new THREE.Vector3(scale, scale, scale))
.setPosition(x, this.getTerrainHeight(x, z), z);
this.batchedMesh.setMatrixAt(batchId, matrix);
}
}UI/信息可视化
javascript
class DataVisualization3D {
constructor(dataPoints) {
this.batchedMesh = new BatchedMesh(
dataPoints.length,
100000,
150000
);
this.colorMap = this.createColorMap();
this.visualizeData(dataPoints);
}
createColorMap() {
// 根据数据值创建渐变色材质
const colors = [
new THREE.Color(0x0000ff), // 低值 - 蓝色
new THREE.Color(0x00ff00), // 中值 - 绿色
new THREE.Color(0xff0000) // 高值 - 红色
];
return colors.map(color =>
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color })
);
}
visualizeData(dataPoints) {
dataPoints.forEach((data, index) => {
// 根据数据类型选择几何体
const geometry = this.getGeometryForDataType(data.type);
// 根据数值选择材质
const materialIndex = Math.floor(
(data.value - data.min) / (data.max - data.min) * this.colorMap.length
);
const batchId = this.batchedMesh.addGeometry(
geometry,
this.colorMap[materialIndex]
);
// 设置位置和大小(基于数据值)
const height = data.value * 10;
const matrix = new THREE.Matrix4()
.makeScale(1, height, 1)
.setPosition(data.x, height/2, data.z);
this.batchedMesh.setMatrixAt(batchId, matrix);
});
}
}javascript
class BatchedMeshPerformanceMonitor {
constructor(batchedMesh) {
this.batchedMesh = batchedMesh;
this.stats = {
drawCalls: 0,
triangleCount: 0,
materialSwitches: 0
};
}
logPerformance() {
const info = this.batchedMesh.info;
console.log('BatchedMesh 性能统计:');
console.log('几何体数量:', info.geometryCount);
console.log('顶点总数:', info.totalVertexCount);
console.log('索引总数:', info.totalIndexCount);
console.log('材质数量:', info.materialCount);
console.log('内存使用(估算):', this.calculateMemoryUsage(), 'MB');
// 对比传统方式
const traditionalDrawCalls = info.geometryCount;
console.log('传统方式 Draw Calls:', traditionalDrawCalls);
console.log('BatchedMesh Draw Calls:', 1); // 理想情况
}
calculateMemoryUsage() {
const info = this.batchedMesh.info;
// 估算内存:顶点数据 + 索引数据 + 矩阵数据
const vertexMemory = info.totalVertexCount * 32; // 每个顶点约32字节
const indexMemory = info.totalIndexCount * 4; // 每个索引4字节
const matrixMemory = info.geometryCount * 64; // 每个矩阵64字节
return ((vertexMemory + indexMemory + matrixMemory) / 1024 / 1024).toFixed(2);
}
}适用条件
javascript
// ✅ 推荐使用 BatchedMesh 的条件:
const shouldUseBatchedMesh = (
objectCount > 100 && // 对象数量多
materialCount > 1 && // 需要多种材质
geometriesAreSimilar && // 几何体相似但不完全相同
!needsIndividualAnimation && // 不需要单独动画
isPerformanceCritical // 性能是关键
);javascript
class BatchedMeshWithLimitations {
constructor() {
// 限制1:动态更新困难
this.solutions = {
// 解决方案:分批次更新
batchUpdates: () => {
// 标记需要更新的批次
this.dirtyBatches = new Set();
// 定期批量更新
setInterval(() => {
if (this.dirtyBatches.size > 0) {
this.batchedMesh.frustumCulled = false;
this.updateDirtyBatches();
this.batchedMesh.frustumCulled = true;
}
}, 100); // 每100ms更新一次
},
// 解决方案2:动态和静态分离
dynamicStaticSeparation: () => {
this.staticBatchedMesh = new BatchedMesh(...); // 静态对象
this.dynamicObjects = new THREE.Group(); // 动态对象
this.dynamicInstancedMeshes = new Map(); // 动态实例化网格
}
};
}
// 限制2:剔除优化
optimizeCulling() {
// BatchedMesh 不支持单独剔除
// 解决方案:按区域分组
const gridSize = 100;
this.gridBatches = new Map();
// 将对象分配到网格单元
objects.forEach(obj => {
const gridKey = `${Math.floor(obj.x/gridSize)},${Math.floor(obj.z/gridSize)}`;
if (!this.gridBatches.has(gridKey)) {
this.gridBatches.set(gridKey, new BatchedMesh(...));
}
this.gridBatches.get(gridKey).addObject(obj);
});
}
}javascript
class BatchedMeshLODSystem {
constructor() {
this.lodLevels = [0, 1, 2]; // 0=高,1=中,2=低
this.batchesByLOD = new Map();
this.lodLevels.forEach(level => {
this.batchesByLOD.set(level, new BatchedMesh(...));
});
this.cameraPosition = new THREE.Vector3();
}
update(camera) {
camera.getWorldPosition(this.cameraPosition);
// 更新每个批次的可见性
this.objects.forEach(obj => {
const distance = obj.position.distanceTo(this.cameraPosition);
const lodLevel = this.getLODLevel(distance);
if (obj.currentLOD !== lodLevel) {
this.moveToLODBatch(obj, lodLevel);
}
});
}
moveToLODBatch(object, targetLOD) {
// 从当前批次移除
if (object.batchId !== undefined) {
const currentBatch = this.batchesByLOD.get(object.currentLOD);
currentBatch.deleteGeometry(object.batchId);
}
// 添加到新批次
const targetBatch = this.batchesByLOD.get(targetLOD);
object.batchId = targetBatch.addGeometry(
object.geometries[targetLOD],
object.material
);
object.currentLOD = targetLOD;
}
}javascript
class CulledBatchedMesh extends BatchedMesh {
constructor(maxGeometryCount, maxVertexCount, maxIndexCount, scene) {
super(maxGeometryCount, maxVertexCount, maxIndexCount, scene);
// 自定义剔除系统
this.visibilityArray = new Float32Array(maxGeometryCount).fill(1);
this.setupVisibilityBuffer();
}
setupVisibilityBuffer() {
// 创建可见性属性缓冲区
const visibilityAttribute = new THREE.InstancedBufferAttribute(
this.visibilityArray,
1
);
this.setAttribute('visibility', visibilityAttribute);
}
updateVisibility(camera) {
const frustum = new THREE.Frustum();
frustum.setFromProjectionMatrix(
new THREE.Matrix4().multiplyMatrices(
camera.projectionMatrix,
camera.matrixWorldInverse
)
);
const matrix = new THREE.Matrix4();
const sphere = new THREE.Sphere();
sphere.radius = 1; // 根据实际调整
for (let i = 0; i < this.geometryCount; i++) {
this.getMatrixAt(i, matrix);
sphere.center.setFromMatrixPosition(matrix);
this.visibilityArray[i] = frustum.intersectsSphere(sphere) ? 1 : 0;
}
this.getAttribute('visibility').needsUpdate = true;
}
}大型静态场景
建筑群、城市景观
自然景观(树木、岩石)
室内装饰品
需要材质多样性的场景
不同类型的地形
彩色数据可视化
游戏中的道具系统
性能关键的应用
WebGL 性能要求高的应用
VR/AR 应用
大规模数据展示
javascript
function chooseOptimizationStrategy(sceneAnalysis) {
const {
objectCount,
materialCount,
needsAnimation,
vertexCount
} = sceneAnalysis;
if (objectCount < 100) {
return '传统单个网格'; // 不需要优化
}
if (materialCount === 1 && !needsAnimation) {
if (vertexCount < 65535) {
return '几何体合并';
} else {
return 'InstancedMesh';
}
}
if (materialCount > 1 && !needsAnimation) {
return 'BatchedMesh'; // 最佳选择
}
if (needsAnimation) {
return 'InstancedMesh + 动态更新';
}
return '混合方案:BatchedMesh + InstancedMesh';
}javascript
// Billboard 基础实现
class BillboardSystem {
constructor() {
this.billboards = new THREE.Group();
this.createBillboardSprites();
}
createBillboardSprites() {
// 方法1:使用 Sprite
const texture = new THREE.TextureLoader().load('tree.png');
const spriteMaterial = new THREE.SpriteMaterial({ map: texture });
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
const sprite = new THREE.Sprite(spriteMaterial);
sprite.position.set(
Math.random() * 100 - 50,
Math.random() * 100 - 50,
Math.random() * 100 - 50
);
sprite.scale.set(5, 5, 1);
this.billboards.add(sprite);
}
// 方法2:使用 Billboard 特性的 Mesh
const geometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(1, 1);
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: texture,
transparent: true,
side: THREE.DoubleSide
});
const billboardMesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
// 在渲染循环中手动更新朝向
}
update(camera) {
// 更新所有 Sprite 朝向相机
this.billboards.children.forEach(sprite => {
sprite.lookAt(camera.position);
});
}
}推荐使用 Billboard 的场景
javascript
class BillboardUseCases {
// 场景1:植被系统(树木、草地)
createVegetationBillboards() {
const treeGroup = new THREE.Group();
// 使用不同角度的树木贴图实现伪3D
const treeTextures = [
this.loadTexture('tree_front.png'),
this.loadTexture('tree_back.png'),
this.loadTexture('tree_side.png')
];
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// 创建交叉的两个平面
const tree = this.createCrossBillboard(treeTextures);
tree.position.set(
Math.random() * 500 - 250,
0,
Math.random() * 500 - 250
);
treeGroup.add(tree);
}
// 优势:
// ✅ 远看效果逼真
// ✅ 性能开销低
// ✅ 易于实现LOD
}
// 场景2:粒子效果
createParticleBillboards() {
const particleCount = 10000;
const particleGroup = new THREE.Group();
const particleTexture = this.createCircleTexture();
const material = new THREE.SpriteMaterial({
map: particleTexture,
transparent: true,
opacity: 0.7,
blending: THREE.AdditiveBlending
});
for (let i = 0; i < particleCount; i++) {
const sprite = new THREE.Sprite(material);
sprite.position.set(
Math.random() * 200 - 100,
Math.random() * 200 - 100,
Math.random() * 200 - 100
);
sprite.scale.setScalar(0.1 + Math.random() * 0.2);
particleGroup.add(sprite);
}
// 优势:
// ✅ 数量极大时性能好
// ✅ 易于动态更新
// ✅ 支持各种混合效果
}
// 场景3:UI元素和图标
createUIBillboards() {
const iconGroup = new THREE.Group();
// 在3D场景中显示2D图标
const icons = ['health', 'ammo', 'map', 'quest'];
icons.forEach((iconType, index) => {
const texture = this.loadTexture(`${iconType}_icon.png`);
const sprite = new THREE.Sprite(
new THREE.SpriteMaterial({ map: texture })
);
sprite.position.set(index * 2 - 3, 5, -10);
sprite.scale.set(1, 1, 1);
iconGroup.add(sprite);
});
// 优势:
// ✅ 始终面向相机
// ✅ 2D图像显示清晰
// ✅ 易于屏幕空间定位
}
}LOD系统中的混合使用
javascript
class HybridLODSystem {
constructor() {
this.nearObjects = new BatchedMesh(200, 50000, 75000); // 近处:3D模型
this.midObjects = new BatchedMesh(500, 30000, 45000); // 中距离:简化模型
this.farObjects = new THREE.Group(); // 远处:Billboard
this.setupLOD();
}
setupLOD() {
// LOD级别定义
this.lodDistances = {
near: 50, // 0-50单位:高细节
mid: 150, // 50-150单位:中细节
far: 500 // 150+单位:Billboard
};
}
addObject(object) {
// 根据距离选择LOD策略
const distance = this.calculateDistanceToCamera(object);
if (distance < this.lodDistances.near) {
this.addToNearBatch(object);
} else if (distance < this.lodDistances.mid) {
this.addToMidBatch(object);
} else {
this.addToFarBillboard(object);
}
}
addToFarBillboard(object) {
// 创建Billboard替代品
const texture = this.createBillboardTexture(object);
const sprite = new THREE.Sprite(
new THREE.SpriteMaterial({ map: texture })
);
sprite.position.copy(object.position);
sprite.scale.set(object.size * 2, object.size * 2, 1);
this.farObjects.add(sprite);
}
updateLOD(cameraPosition) {
// 动态更新LOD级别
this.objects.forEach(object => {
const newDistance = object.position.distanceTo(cameraPosition);
const currentLOD = object.currentLOD;
const targetLOD = this.getLODLevel(newDistance);
if (currentLOD !== targetLOD) {
this.moveObjectToLOD(object, targetLOD);
}
});
}
}javascript
class DynamicStaticSeparation {
constructor() {
// 静态对象:使用 BatchedMesh
this.staticBatch = new BatchedMesh(1000, 200000, 300000);
// 动态对象:使用 Billboard(如果需要面向相机)
this.dynamicBillboards = new THREE.Group();
// 或使用 InstancedMesh(如果需要3D但动态)
this.dynamicInstanced = new Map();
this.setupScene();
}
setupScene() {
// 静态环境:建筑、地形
this.createStaticEnvironment();
// 动态元素:NPC、车辆、特效
this.createDynamicElements();
}
createStaticEnvironment() {
// 使用 BatchedMesh 合并所有静态对象
const staticObjects = this.getAllStaticObjects();
staticObjects.forEach(obj => {
const batchId = this.staticBatch.addGeometry(
obj.geometry,
obj.material
);
this.staticBatch.setMatrixAt(batchId, obj.matrix);
});
}
createDynamicElements() {
// NPC:使用Billboard(如果从远处看)
this.createNPCBillboards();
// 车辆:使用InstancedMesh(需要3D效果)
this.createVehicleInstances();
// 特效:使用粒子系统(Billboard)
this.createEffectParticles();
}
createNPCBillboards() {
// 为每个NPC创建Billboard
this.npcs.forEach(npc => {
const texture = this.getNPCTexture(npc.type);
const sprite = new THREE.Sprite(
new THREE.SpriteMaterial({ map: texture })
);
sprite.position.copy(npc.position);
this.dynamicBillboards.add(sprite);
npc.sprite = sprite;
});
}
updateDynamicElements(deltaTime) {
// 更新Billboard位置和朝向
this.npcs.forEach(npc => {
// 更新位置
npc.sprite.position.add(npc.velocity.clone().multiplyScalar(deltaTime));
// Billboard自动面向相机,无需手动更新朝向
});
}
}** Billboard 优化技巧**
javascript
class BillboardOptimization {
constructor() {
this.optimizedBillboards = this.createOptimizedBillboards();
}
createOptimizedBillboards() {
// 优化1:使用共享材质
const sharedMaterial = new THREE.SpriteMaterial({
map: this.createAtlasTexture(),
transparent: true
});
// 优化2:按距离分组
const billboardGroups = {
near: new THREE.Group(),
mid: new THREE.Group(),
far: new THREE.Group()
};
// 优化3:视锥体剔除
this.setupFrustumCulling(billboardGroups);
// 优化4:LOD纹理
this.setupTextureLOD();
return billboardGroups;
}
setupTextureLOD() {
// 为不同距离使用不同分辨率的纹理
this.textureLOD = {
high: this.loadTexture('tree_high.png'), // 2048x2048
medium: this.loadTexture('tree_med.png'), // 1024x1024
low: this.loadTexture('tree_low.png') // 512x512
};
}
}javascript
// 决策函数:根据需求选择技术
function chooseTechnique(requirements) {
const {
objectCount,
needs3DGeometry,
materialVariety,
needsDynamicUpdate,
cameraFacingRequired,
performanceCritical
} = requirements;
// 决策流程
if (cameraFacingRequired && !needs3DGeometry) {
// 需要面向相机且不需要3D几何体
return {
technique: 'Billboard',
reason: '最适合始终面向相机的2D元素',
implementation: 'THREE.Sprite 或手动朝向的 Plane'
};
}
if (objectCount > 1000 && materialVariety > 1) {
// 大量对象且需要多种材质
return {
technique: 'BatchedMesh',
reason: '高效处理大量多材质对象',
implementation: 'THREE.BatchedMesh'
};
}
if (needsDynamicUpdate && objectCount > 100) {
// 需要动态更新且对象较多
if (cameraFacingRequired) {
return {
technique: 'Billboard',
reason: '动态更新性能更好',
implementation: 'THREE.Sprite'
};
} else {
return {
technique: 'InstancedMesh',
reason: '支持动态更新的3D对象',
implementation: 'THREE.InstancedMesh'
};
}
}
if (needs3DGeometry && performanceCritical) {
// 需要3D几何体且性能关键
if (materialVariety === 1) {
return {
technique: 'InstancedMesh',
reason: '单材质3D对象的最佳性能',
implementation: 'THREE.InstancedMesh'
};
} else {
return {
technique: 'BatchedMesh',
reason: '多材质3D对象的性能优化',
implementation: 'THREE.BatchedMesh'
};
}
}
// 默认:传统单个Mesh
return {
technique: 'Individual Meshes',
reason: '对象数量少,简单直接',
implementation: '多个 THREE.Mesh'
};
}
// 使用示例
const myRequirements = {
objectCount: 500,
needs3DGeometry: false,
materialVariety: 1,
needsDynamicUpdate: true,
cameraFacingRequired: true,
performanceCritical: true
};
const decision = chooseTechnique(myRequirements);
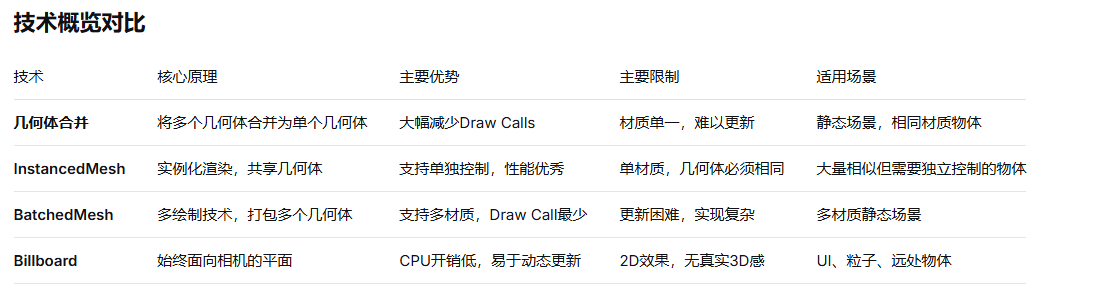
console.log(decision);Billboard 优势:
始终面向相机,适合UI、粒子、远处物体
CPU开销低,易于动态更新
适合大量简单2D元素
2D元素:Billboard
javascript
class PerformanceMonitor {
constructor() {
this.monitorTechniques();
}
monitorTechniques() {
// 监控不同技术的性能
setInterval(() => {
const renderInfo = renderer.info.render;
console.table({
'Draw Calls': renderInfo.calls,
'Triangles': renderInfo.triangles,
'Textures': renderInfo.textures,
'Geometries': renderInfo.geometries,
'Frame Time': this.getFrameTime()
});
}, 1000);
}
compareTechniques(techniqueA, techniqueB) {
// A/B测试不同技术
return {
'Draw Call减少': `${((techniqueA.calls - techniqueB.calls) / techniqueA.calls * 100).toFixed(1)}%`,
'内存减少': `${((techniqueA.memory - techniqueB.memory) / techniqueA.memory * 100).toFixed(1)}%`,
'帧率提升': `${((techniqueB.fps - techniqueA.fps) / techniqueA.fps * 100).toFixed(1)}%`
};
}
}
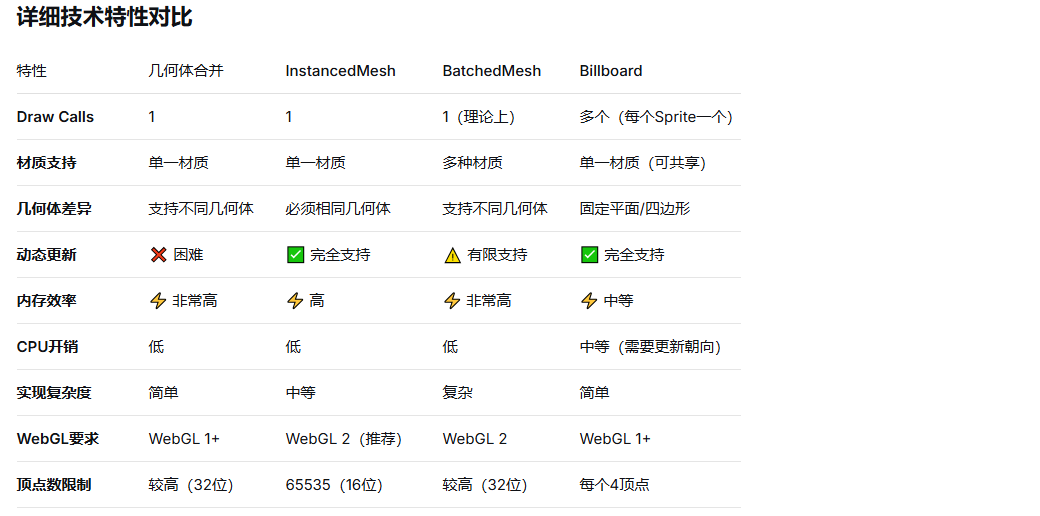
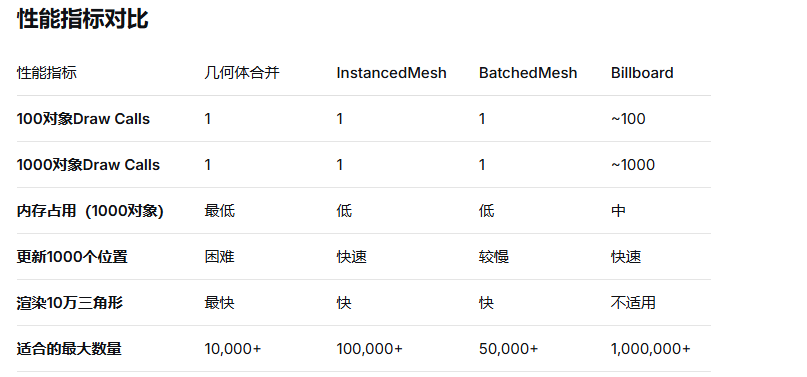
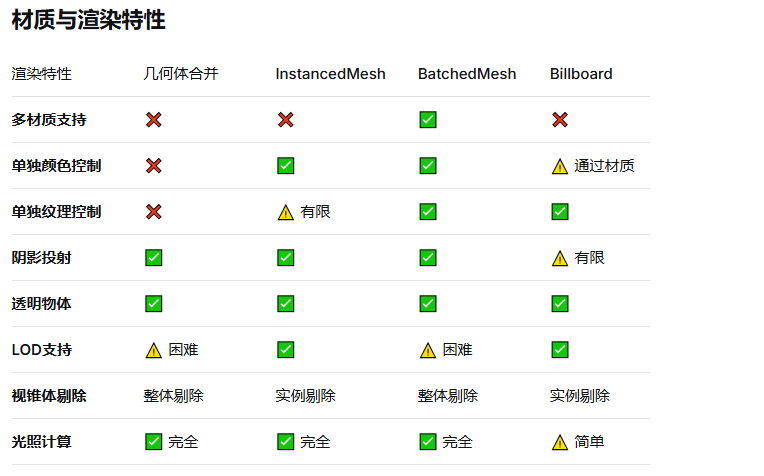
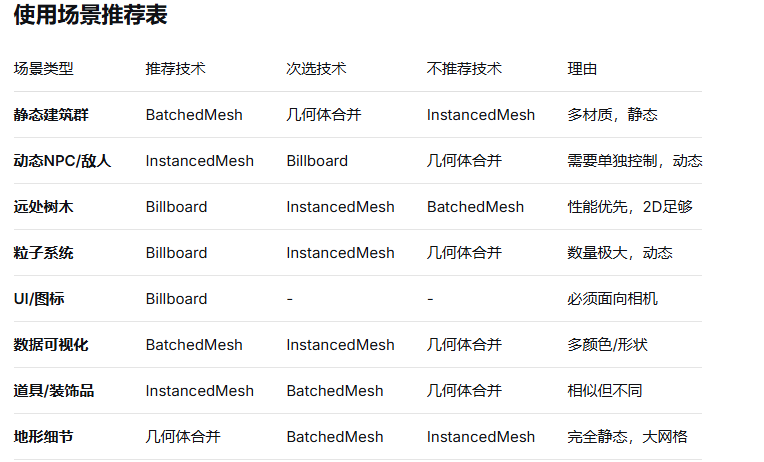
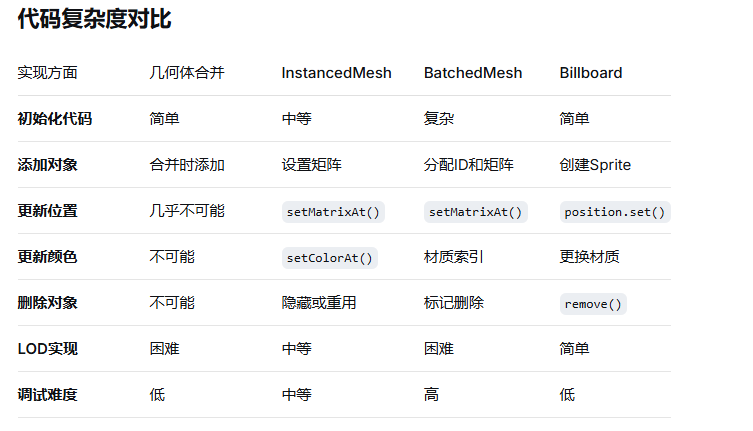
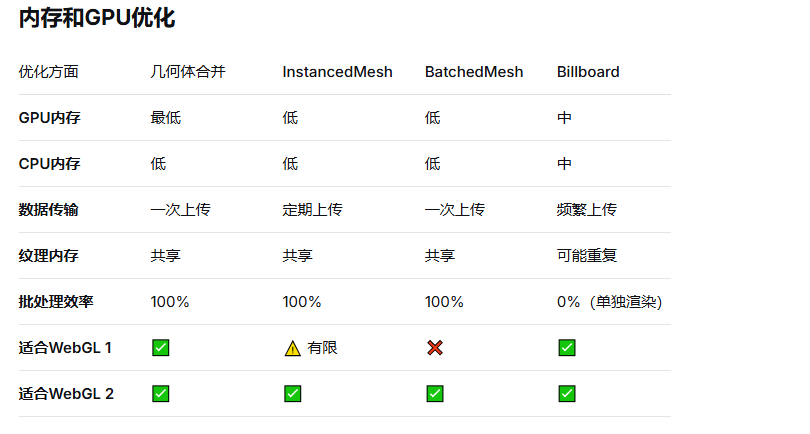
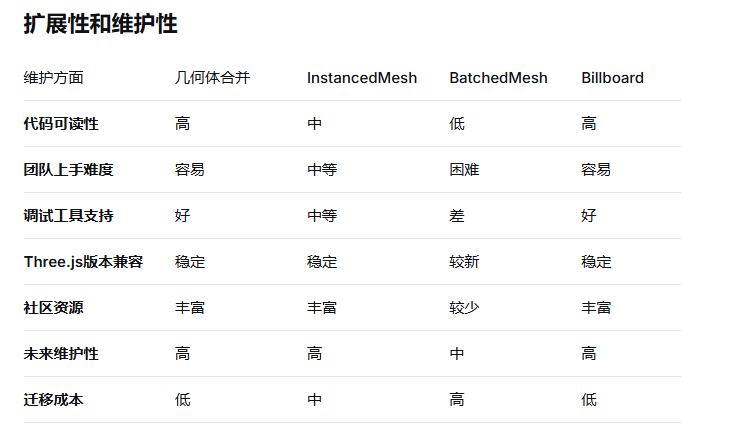
物体完全静态,不会移动
所有物体使用相同材质
物体数量中等(< 10,000)
需要最简单的实现
物体需要单独控制(位置、旋转、颜色)
所有物体几何形状相同
使用单一材质
物体数量非常多(> 1,000)
物体使用多种不同材质
物体几何形状不同
物体基本静态
追求最佳性能(Draw Call最少)
物体需要始终面向相机
使用2D图像足够表现
物体数量极大(> 10,000)
需要频繁动态更新